This introduction describes an iterative model that forms the basis of a systems approach to health and care design and continuous improvement.
Contents
Introduction
Activities are an important part of any toolkit, but are only as good as the people that use them and only effective when used to accomplish appropriate activities. Activities in the hands of novices may require careful instruction or benefit from some form of training or apprenticeship. Activities in the hands of experts may feel like an extension of the master working their trade, used for their intended purpose or adapted for other purposes. Activities are typically designed with a number of specific tools in mind and optimised for a particular purpose, however, many may be usefully adopted for related tasks.
The activities in this toolkit are largely off-the-shelf, established and well used. Simple guidance is provided for their use and reference given to resources that describe them in more detail. The intention is not to provide full instructions for their use here, rather to point to their existence and indicate where they might be used. They are ordered according to their most likely contribution to the key strands of the Improvement Model that they relate to, but may be used at any stage. Hence the activities are presented in groups, aligned with the key strands, but are also listed here alphabetically.
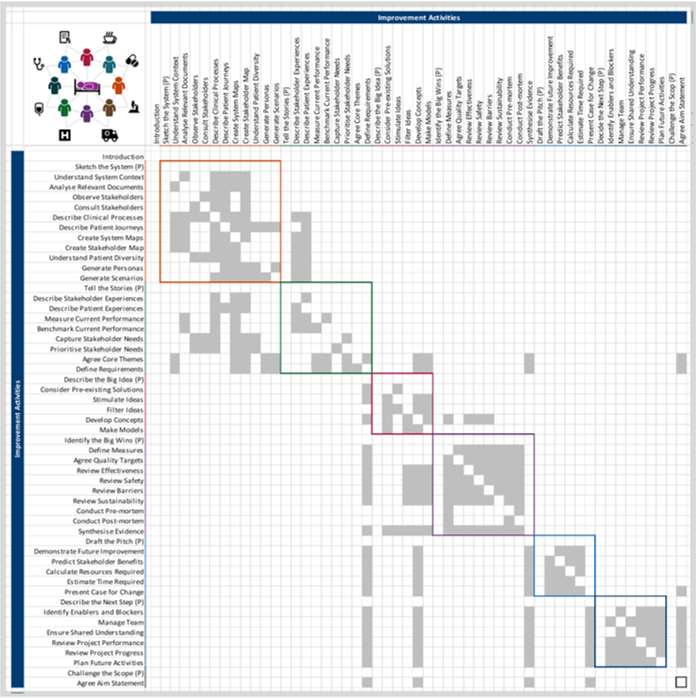
Activities may be mapped to activities to assist in their selection. More than one activity may be used for any particular purpose and this is often encouraged. The mapping provides clear indication as to how some activities might be used to support others, but is not expected to exhaustively show where activities may be linked in practice.
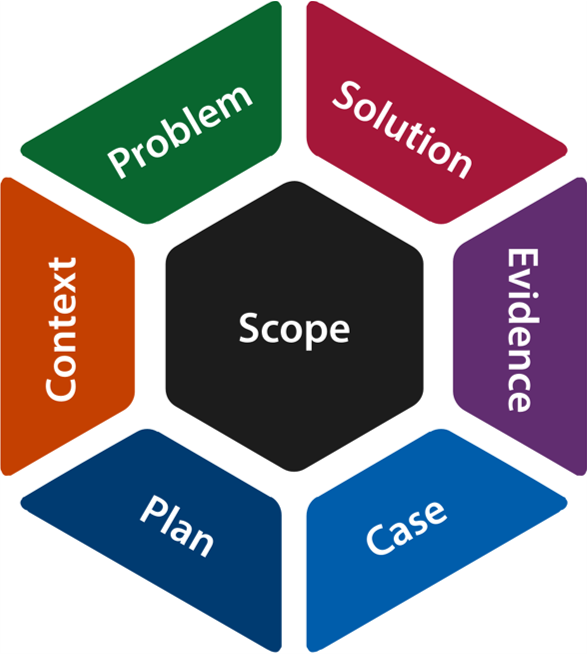
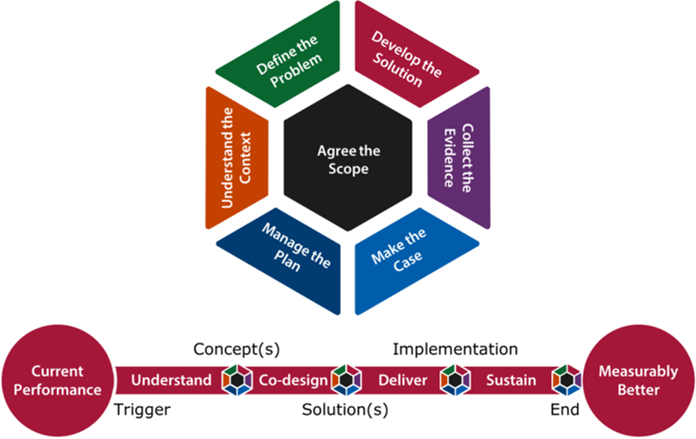
As already seen in the Improving Improvement section of this toolkit, the heart of this toolkit integrates the key questions from the Engineering Better Care report together with an Improvement Model that contains seven activity strands, together with the depiction of the Improvement Stages within the improvement process.
As described previously in the Engineering Better Care section, the activity strands that focus on particular aspects of a successful improvement process include:
- Understand the Context — describes the circumstances or setting that surround a system and all the factors that could influence the system and its improvement.
- Define the Problem — describes the detail of a particular challenge within a system and all the requirements for change necessary to improve the system.
- Develop the Solution — describes a way of solving a particular problem within a system and all the elements of change necessary to improve the system.
- Collect the Evidence — describes the information and all the measures used to evidence the validity of a particular solution(s) to a problem within a system.
- Make the Case — describes the set of facts or arguments in support of improving a system and delivering a particular solution(s) to a problem within the system.
- Manage the Plan — describes a detailed proposal for enabling change to a system and delivering a particular solution(s) to a problem within the system.
- Agree the Scope — describes the context of the improvement envisaged in terms of the extent of the ambition for improvement and the boundary of the system of interest.
The following sections describe the activities associated with the context, problem, solution, evidence, case, plan and scope strands associated with the Improvement Model. In each case, a brief introduction to the strand is provided, along with details of all the activities related to that strand and tools that may be used to support those activities. An introduction to the literature related to each strand is also provided.
Useful toolkit resources: Cards for each of these activities are included in the Resources part of this toolkit. A number of blank cards are included to allow additional activities to be added.
Text list of Activities
Context
Problem
- Tell the Stories
- Describe Stakeholder Experiences
- Describe Patient Experiences
- Measure Current Performance
- Benchmark Current Performance
- Capture Stakeholder Needs
- Prioritise Stakeholder Needs
- Agree Core Themes
- Define Requirements
Solution
Pictorial list of Activities
You can click on any of the images below to find out more about that activity.
Cards for each of the activities are available in the boxed version of this toolkit. If you would like further information on how to get hold of these cards, please contact edc-toolkit@eng.cam.ac.uk
Context
Understanding the context is critical to the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important at the beginning of the improvement process and should be reviewed regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process are described within the Improvement Stages section, and each stage will most likely comprise a number of preliminary activities, followed by specific stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the context strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Sketch the System. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the context should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The full set of possible activities within the context strand are: Understand System Context, Analyse Relevant Documents, Observe Stakeholders, Consult Stakeholders, Describe Clinical Processes, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Understand Patient Diversity, Generate Personas and Generate Scenarios. If any of these have been undertaken before the start of the project, they should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
The Stage Plan should be used to identify the outputs and deliverables that are required for each stage, and the possible activities that need to be completed. Each improvement stage has its own Stage Guide, which provides guidance on activities that could be selected.
All the activities for the context strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Sketch the System
This preliminary activity encourages people to show the relationships between all the elements, people, locations, conditions, tasks and information and deliver a sketch or rich picture describing what is known about the system and its context.
Tools: Soft Systems Method, Entity Relationship Diagram
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Top tips:
- Use shapes to describe system elements and people
- Use labelled arrows to describe the relationships between them
- Use multiple diagrams to show different perspectives
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Understand System Context
The location of the system in its wider geographical, political, management and cultural context.
Purpose: to understand the management, policy and political landscape within which the system exists
Inputs: Analyse Relevant Documents, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys
Tools: Entity Relationship Diagram
Outputs: a comprehensive description of the wider geographical, political, management and cultural context of the system
Top tips:
- Describe the geographical and political context of the system
- Describe the management and leadership context of the system
- Understand local practice and policy on improvement and innovation
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Analyse Relevant Documents
The analysis of documents relating to the system of interest, to reveal the current extent, behaviour and performance of the system
Purpose: to understand the system of interest, its context, stakeholders, elements and performance
Inputs: Understand System Context, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys
Tools: Literature Review
Outputs: a compendium of relevant documents and commentary on their content and likely influence on the improvement
Top tips:
- Collect documents relevant to the system of interest
- Identify other literature of relevance to the system
- Analyse the documents and literature
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Observe Stakeholders
The observation of individual stakeholders, i.e. service providers and users, to better understand their experiences of care
Purpose: to observe stakeholders within the system and document their actual behaviour
Inputs: Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys, Consult Stakeholders
Tools: Participant Observation, Observational Study, Spaghetti Diagram
Outputs: a description of the actual behaviour and journeys undertaken by individual stakeholders
Top tips:
- Use a variety of observation and ethnographic tools
- Select a representative sample of stakeholders
- Observe links with other stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Consult Stakeholders
The consultation of individual stakeholders, i.e. service providers or users, to better understand their needs and experiences of care
Purpose: to consult stakeholders within the system and understand their expected behaviour
Inputs: Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys, Observe Stakeholders
Tools: One-to-one Interviews, Facilitated Discussion, Delphi Study
Outputs: a description of the expected behaviour and journeys undertaken by individual stakeholders
Top tips:
- Use a variety of interview, discussion and survey tools
- Select a representative sample of stakeholders
- Consult on links with other stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Describe Clinical Processes
The mapping of the clinical processes that make up and support the patient journey through the system of interest
Purpose: to describe the clinical processes, key decisions and expected outcomes associated with the system
Inputs: Understand System Context, Analyse Relevant Documents, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Patient Journeys, Observe Stakeholders, Consult Stakeholders, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences
Tools: Literature Review, Rich Picture, Soft Systems Method, Entity Relationship Diagram, Data Flow Diagram, State Transition Diagram, Flow Chart, Swimlane Diagram, Spaghetti Diagram, Storyboarding
Outputs: a description of clinical processes, highlighting the key stages and any particular challenges that might be faced
Top tips:
- Convene a representative group of service stakeholders
- Think broadly to identify where the stakeholder journeys begin
- Consider all stages of the subsequent stakeholder journeys
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Describe Patient Journeys
The mapping of the patient journeys associated with particular clinical processes within the system of interest
Purpose: to describe the patient journeys through the system associated with particular clinical processes
Inputs: Understand System Context, Analyse Relevant Documents, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Observe Stakeholders, Consult Stakeholders, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences
Tools: Soft Systems Method, Entity Relationship Diagram, State Transition Diagram, Flow Chart, Swimlane Diagram, Spaghetti Diagram, Life Café, Public Involvement, Storyboarding
Outputs: a description of patient journeys, highlighting the key stages and any particular challenges that might be faced
Top tips:
- Convene a representative group of patients or their representatives
- Think broadly to identify where the patient journey begins
- Consider all stages of the subsequent patient journey
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Create System Maps
The mapping of the system of interest, to identify key elements and their interfaces to each other and neighbouring systems
Purpose: to create a common view of the system, its elements, architecture and interfaces to other systems
Inputs: Understand System Context, Analyse Relevant Documents, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences
Tools: Literature Review, Rich Picture, Soft Systems Method, Causal Loop Diagram, Influence Map, Entity Relationship Diagram, Data Flow Diagram, State Transition Diagram, Flow Chart, Swimlane Diagram, Dependency Structure Matrix
Worksheets: Rich Picture, Influence Map, Data-flow Diagram
Outputs: a set of maps of the system, its elements and their interfaces to each other and other systems
Top tips:
- Include anything that can impact on the desired outcomes
- Link to stakeholder map, clinical pathway and patient journeys
- Reflect on what is noteworthy about the location of the system
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Create Stakeholder Map
The mapping of the links between stakeholders, i.e. service providers or users, who have a direct or indirect interest in the system to be improved
Purpose: to create a common view of the range of stakeholders, their interests, and the links between them
Inputs: Understand System Context, Analyse Relevant Documents, Create System Maps, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences
Tools: Literature Review, Rich Picture, Soft Systems Method, Causal Loop Diagram, Influence Map, Entity Relationship Diagram, Swimlane Diagram, Dependency Structure Matrix
Worksheets: Stakeholder List, Stakeholder Influence, Stakeholder Needs, Stakeholder Map
Cards: Service Users, Service Stakeholders
Outputs: a map of the system stakeholders, their interests and the links between them
Top tips:
- List stakeholders starting with those at the heart of the system
- Describe the likely interests of the stakeholders in the system
- Identify links through formal and informal networks and pathways
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Understand Patient Diversity
The acknowledgement of the diversity of patients and their corresponding journeys and experiences of care
Purpose: to understand the diversity of patients within the system and their particular needs and capabilities
Inputs: Create System Maps, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys, Observe Stakeholders, Consult Stakeholders, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences
Tools: One-to-One Interviews, Facilitated Discussion, Participant Observation, Observational Study
Cards: Service Users
Outputs: a description of the diversity of patients and their experiences of care
Top tips:
- Consider the range of patients navigating the user journey
- Expect to see diversity in sensory, cognitive and motion capability
- Expect to see diversity in gender, culture and socioeconomic status
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Generate Personas
The drafting of short, narrative descriptions of people, as providers or recipients of care, to inspire and test ideas for improvement
Purpose: to describe stereotypical patients or care providers, with a range of medical conditions and capabilities
Inputs: Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Understand Patient Diversity, Describe Patient Journeys, Generate Scenarios, Describe Stakeholder Experiences, Describe Patient Experiences
Tools: Designing Personas
Cards: Service Users, Service Stakeholders
Outputs: a set of personas that are representative of the range or possible users of the system
Top tips:
- Ensure personas emphasise notable user characteristics
- Generate a set of personas to caricature the diversity of users
- Use personas as a means to test ideas for improvement
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Generate Scenarios
The drafting of short, narrative descriptions of a range of scenarios of care to inspire and test ideas for improvement
Purpose: to describe stereotypical scenarios of care involving a range of typical patients and care providers
Inputs: Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Journeys, Understand Patient Diversity, Generate Personas, Describe Stakeholder Experiences, Describe Patient Experiences
Tools: Designing Scenarios
Cards: Service Users, Service Stakeholders
Outputs: a set of scenarios that are representative of the range of possible journeys through the system
Top tips:
- Ensure scenarios emphasise notable pathway characteristics
- Generate a set of scenarios to caricature the diversity of care
- Use scenarios as a means to test ideas for improvement
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Problem
Defining the problem is vital for the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important at the beginning of the improvement process and should be reviewed regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process were previously described within the Improvement Stages section, where each stage will likely comprise a preliminary activity, followed by a number of stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the problem strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Tell the Stories. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the problem should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The full set of possible activities within the problem strand are : Describe Stakeholder Experiences, Describe Patient Experiences, Measure Current Performance, Benchmark Current Performance, Capture Stakeholder Needs, Prioritise Stakeholder Needs, Agree Core Themes and Define Requirements. If any of these activities have been undertaken before the start of the project, they should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
The Stage Plan should be used to identify the outputs and deliverables that are required for each stage, and the possible activities that need to be completed. Each improvement stage has its own Stage Guide, which provides guidance on activities that could be selected.
All the activities for the problem strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Tell the Stories
This preliminary activity encourages people to communicate stories of patient and stakeholder experiences that bring life to the improvement challenges and deliver a description of what is known about the current challenges within the system.
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Cards: Service Users, Service Stakeholders
Top tips:
- Bring stories to life with images and videos of interviews
- Use the stories to identify key elements of the system
- Showcase areas of the system that might be improved
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Describe Stakeholder Experiences
The description of stakeholder journeys, using observation and consultation approaches, to understand their experiences
Purpose: to capture stakeholder experiences of their varied and multiple journeys through the system
Inputs: Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Experiences
Tools: One-to-One Interviews, Facilitated Discussion, Delphi Study, Life Café, Public Involvement, Storyboarding
Worksheets: Design Wall
Cards: Service Stakeholders
Outputs: a description of stakeholder experiences, highlighting the key stages and particular challenges that might be faced
Top tips:
- Convene a representative group of service stakeholders
- Collect stakeholder stories identifying the elements of care
- Discuss different experiences of the service and patients
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Describe Patient Experiences
The description of patient journeys, using observation and consultation approaches, to understand their experiences
Purpose: to capture patients’ experiences of their care journeys through the system
Inputs: Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Stakeholder Experiences
Tools: One-to-One Interviews, Facilitated Discussion, Life Café, Public Involvement, Storyboarding
Worksheets: Design Wall
Cards: Service Users
Outputs: a description of patient experiences, highlighting the key stages and any particular challenges that might be faced
Top tips:
- Convene a representative group of patients or their representatives
- Collect patient stories identifying the elements of care
- Discuss different experiences of the process and associated care
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Measure Current Performance
The collection and analysis of recent measured performance data and targets, including both quantitative and qualitative data
Purpose: to measure current levels of performance, taking account of the prioritised stakeholder needs
Inputs: Analyse Relevant Documents, Create System Maps, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences, Benchmark Current Performance
Tools: Observational Study, Data Analysis
Outputs: measured qualitative and quantitative performance data relating to the system of interest and its stakeholders
Top tips:
- Monitor the current performance of the whole system
- Estimate the levels of performance from qualitative measures
- Derive the levels of performance from quantitative measures
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Benchmark Current Performance
The collection and analysis of recent performance data and targets, benchmarked where appropriate to similar systems
Purpose: to analyse current levels of performance, taking account of the prioritised stakeholder needs
Inputs: Analyse Relevant Documents, Create System Maps, Describe Clinical Processes, Describe Patient Experiences, Describe Stakeholder Experiences, Measure Current Performance
Tools: Facilitated Discussion, Observational Study, Data Analysis
Outputs: performance data relating to the system of interest and its stakeholders, and benchmarking to similar systems
Top tips:
- Convene a representative group of stakeholders together
- Present recent information and benchmark the elements of care
- Discuss different perspectives on the current performance
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Capture Stakeholder Needs
The capture of stakeholder needs relating to the purpose of the system, detailing the rationale for each individual need
Purpose: to identify the full range of possible stakeholder needs relevant to the system
Inputs: Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Observe Stakeholders, Consult Stakeholders, Understand Patient Diversity, Prioritise Stakeholder Needs
Tools: One-to-one Interviews, Facilitated Discussion, Delphi Study, Participant Observation, Observational Study, Designing Personas, Designing Scenarios, MoSCoW, Data Analysis, Storyboarding
Cards: Service Stakeholders
Outputs: a full list of stakeholders’ needs, including the rationale for each need
Top tips:
- Capture and explore as many of the needs as possible
- Describe the needs without suggesting possible solutions
- Use a system map to assist identification of system needs
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Prioritise Stakeholder Needs
The prioritisation of stakeholder needs relating to the purpose of the system, detailing the rationale for each priority
Purpose: to understand the relative priority of stakeholder needs relevant to the system
Inputs: Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Describe Clinical Processes, Observe Stakeholders, Consult Stakeholders, Understand Patient Diversity, Capture Stakeholder Needs
Tools: Value Stream Mapping, Dependency Structure Matrix, One-to-one Interviews, Facilitated Discussion, Delphi Study, Designing Personas, Designing Scenarios, MoSCoW
Outputs: a prioritized list of stakeholders’ needs, including the rationale for each need
Top tips:
- Prioritise the stakeholders needs resolving any conflicts
- Focus on outcomes and their values to the stakeholders
- Develop requirements with the prioritised list in mind
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Agree Core Themes
The identification and articulation of the core themes for the requirements for improvement, describing what the revised system must do
Purpose: to agree the core themes for the requirements based on the prioritised stakeholder needs
Inputs: Understand System Context, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Generate Personas, Generate Scenarios, Prioritise Stakeholder Needs, Benchmark Current Performance, Measure Current Performance, Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Synthesise Evidence, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: Value Stream Mapping, Dependency Structure Matrix, Delphi Study, Life Café, Public Involvement, MoSCoW, Fishbone Diagram
Outputs: a short list of specific, measurable, acceptable, realistic themes to act as a the focus for the improved system
Top tips:
- Be specific, measurable, acceptable, realistic and time-bound
- Capture the essence of what the system must do
- Link the core themes to appropriate stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Define Requirements
The definition of requirements for improvement, describing what the revised system should be able to do and how this will be measured
Purpose: to elaborate on the core themes to develop a detailed set of system requirements
Inputs: Understand System Context, Create System Maps, Create Stakeholder Map, Generate Personas, Generate Scenarios, Prioritise Stakeholder Needs, Benchmark Current Performance, Measure Current Performance, Agree Core Themes, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Synthesise Evidence, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: Value Stream Mapping, Delphi Study, Life Café, Public Involvement, MoSCoW, Fishbone Diagram
Worksheets: Design Requirements
Outputs: a prioritised list of specific, measurable, acceptable, realistic and time-bound requirements for the improved system
Top tips:
- Be specific, measurable, acceptable, realistic and time-bound
- Distinguish between demands and wishes
- Link all requirements to appropriate themes
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Solution
Developing the solution is essential for the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important in the middle of the improvement process and should be reviewed regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process are described within the Improvement Stages section, and each stage will most likely comprise a number of preliminary activities, followed by specific stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the solution strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Describe the Big Idea. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the solution should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The full set of possible activities within the solution strand are: Consider Pre-existing Solutions, Stimulate Ideas, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts and Make Models. If any of these have been undertaken before the start of the project, they should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
The Stage Plan should be used to identify the outputs and deliverables that are required for each stage, and the possible activities that need to be completed. Each improvement stage has its own Stage Guide, which provides guidance on activities that could be selected.
All the activities for the solution strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Describe the Big Idea
This preliminary activity encourages people to think creatively and describe how the system could be improved and deliver a description of what is proposed as a possible solution concept(s) for improving the system.
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Top tips:
- Establish a creative culture for generating ideas
- Identify ideas that are most likely to result in improvement
- Use sketches or models to bring the idea(s) to life
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Consider Pre-existing Solutions
The identification, review and presentation of existing solutions with the potential to satisfy the demands of the requirements
Purpose: to consider pre-existing solutions that have the potential to meet the system requirements
Inputs: Define Requirements, Stimulate Ideas
Tools: Morphological Chart
Outputs: a list of pre-existing solutions with potential to satisfy the demands of the requirements
Top tips:
- Allow plenty of time for solution identification and review
- Ensure pre-existing solutions meet the demands in the requirements
- Avoid fixation to encourage a broader search
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Stimulate Ideas
The generation of ideas to inspire the creation of new ideas that are likely to satisfy the demands of the requirements
Purpose: to stimulate ideas that may lead to new concepts that meet the system requirements
Inputs: Define Requirements, Consider Pre-existing Solutions, Develop Concepts, Make Models
Tools: Storyboarding, Brainstorming, Disney, Six Thinking Hats
Worksheets: Morphological Chart, Design Ideas
Outputs: a wide range of ideas with the potential to lead to new concepts that may satisfy the demands of the requirements
Top tips:
- Adopt a variety of methods to encourage the generation of ideas
- Consider the use of tools that avoid fixation and encourage creativity
- Include all ideas generated at this stage, filter later
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Filter Ideas
The filtering of ideas to ensue the development of new concepts with the potential to satisfy the demands of the requirements
Purpose: to evaluate new ideas against the demands and wishes in the system requirements
Inputs: Consider Pre-existing Solutions, Stimulate Ideas, Develop Concepts, Make Models
Tools: Morphological Chart
Outputs: a range of ideas with the potential to lead to new concepts that satisfy the demands of the requirements
Top tips:
- Ensure ideas meet the demands in the requirements
- Filter ideas against the wishes in the requirements
- Note requirements that relate to different stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Develop Concepts
The development of new concepts with the potential to satisfy the demands and meet the wishes of the system requirements
Purpose: to develop new concepts that have the potential to meet the system requirements
Inputs: Define Requirements, Consider Pre-existing Solutions, Stimulate Ideas, Make Models, Define Measures, Review Barriers, Review Safety, Review Effectiveness
Tools: Brainstorming, Disney, Six Thinking Hats, Morphological Chart
Outputs: a number of new concepts that are likely to satisfy the demands and meet the wishes of the requirements
Top tips:
- Allow plenty of time for concept development
- Combine elements of different ideas to develop new concepts
- Avoid fixation to encourage greater creativity
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Make Models
The early evaluation of new concepts to see if they satisfy the demands and meet the wishes of the requirements
Purpose: to make models of new concepts to enable early evaluation against the system requirements
Inputs: Consider Pre-existing Solutions, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts
Outputs: a number of models and evidence of their behaviour against the demands and wishes of the requirements
Top tips:
- Produce a physical or virtual demonstration of the concept
- Consider different models for different purposes
- Consider quick tests with rough models to resolve critical issues
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Evidence
Collecting the evidence is key to the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important early in the improvement process and should be updated regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process are described within the Improvement Stages section, and each stage will most likely comprise a number of preliminary activities, followed by specific stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the evidence strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Identify the Big Wins. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the evidence should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The full set of possible activities within the evidence strand are: Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Effectiveness, Review Safety, Review Barriers and Synthesise Evidence. If any of these have been undertaken before the start of the project, they should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
The Stage Plan should be used to identify the outputs and deliverables that are required for each stage, and the possible activities that need to be completed. Each improvement stage has its own Stage Guide, which provides guidance on activities that could be selected.
All the activities for the evidence strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Identify the Big Wins
This preliminary activity encourages people to identify the big wins and justify the resources required to make the system changes proposed and deliver a description of the most likely outcome(s) from delivering the proposed solution(s) for improving the system.
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Top tips:
- Quantify how many patients could benefit from the changes
- Identify the potential benefits, costs and risks for the stakeholders
- Consider the alignment of risks and benefits for each stakeholder
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Define Measures
The translation of the core themes for improvement into the definition of appropriate and robust measures of success
Purpose: to define performance measures to evidence the successful delivery of a measurably better system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Agree Quality Targets, Review Effectiveness, Review Safety, Review Barriers, Review Sustainability
Worksheets: Design Measurement
Outputs: a clear definition of the performance measures required to evidence success
Top tips:
- Establish a clear rationale for the criteria for success
- Identify performance measures necessary to demonstrate success
- Align evaluation activities to the measures and criteria
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Agree Quality Targets
The translation of the core themes for improvement into the definition of appropriate and robust quality targets to ensure success
Purpose: to define service quality targets to ensure the successful delivery of a measurably better system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Define Measures, Review Effectiveness, Review Safety, Review Barriers, Review Sustainability
Outputs: a clear definition of the quality targets required to ensure success
Top tips:
- Define appropriate targets for clinical and cost effectiveness
- Define appropriate targets for patient safety
- Define appropriate targets for patient experience
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Review Effectiveness
The systematic review of new concepts, identifying their strengths and weaknesses in meeting the prioritised stakeholder needs
Purpose: to identify clinical and cost effectiveness risks in the adoption of new concepts by their intended users
Inputs: Define Requirements, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Safety, Review Barriers, Review Sustainability
Tools: Exclusion Audit, Expert Review, User Trials
Outputs: a list of the strengths and weaknesses of the new concepts in meeting the stakeholder needs
Top tips:
- Ensure concepts meet the demands in the requirements
- Check if concepts meet the wishes in the requirements
- Note requirements that relate to different stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Review Safety
The systematic review of the safety of the system, identifying hazards and the subsequent risks they pose to users
Purpose: to identify safety concerns in the adoption of new concepts by their intended users
Inputs: Define Requirements, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Effectiveness, Review Barriers, Review Sustainability
Tools: Root Cause Analysis, Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, Fault Tree Analysis, Hazard and Operability Analysis, Structured What-if Technique, Bowtie Method, Risk Matrix
Worksheets: Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, Structured What If Technique, Bowtie Method, Risk Issues
Outputs: a list of the hazards present within the proposed system and the safety risk they pose to users
Top tips:
- List the hazards presented to users along the care journey
- Estimate the likelihood of harm posed by these hazards
- Identify the likely extent of harm posed by these hazards
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Review Barriers
The systematic review of the demands made by the system on patients and other stakeholders, and their corresponding capability to respond
Purpose: to identify potential barriers to the adoption of new concepts by their intended users
Inputs: Define Requirements, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Effectiveness, Review Safety, Review Sustainability
Tools: Exclusion Audit, Expert Review, User Trials
Worksheets: Design Wall
Outputs: a list of accessibility issues with the proposed system and the challenge they pose to users
Top tips:
- Understand the demands made of users along the care journey
- Estimate the users’ capability to respond to these demands
- Identify where specific demands exceed users’ capabilities
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Review Sustainability
The systematic review of the sustainability of the system, identifying issues and the subsequent impacts to users and the environment
Purpose: to identify sustainability concerns in the adoption of new concepts by their intended users
Inputs: Define Requirements, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Effectiveness, Review Safety, Review Barriers
Tools: Life Cycle Assessment
Outputs: a list of sustainability issues with the proposed system and the impacts to users and the environment
Top tips:
- List the sustainability issues that arise along the care journey
- Estimate the likelihood of adverse impacts posed by these issues
- Identify the likely extent of adverse impacts posed by these issues
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Conduct Pre-mortem
The pre-emptive assessment of the potential for a project to fail, using prospective hindsight to foresee future challenges
Purpose: to Identify those things that could potentially lead to the failure or success of the proposed improvement
Inputs: Agree Aim Statement, Prioritise Stakeholder Needs, Agree Core Themes, Define Requirements, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Present Case for Change, Ensure Shared Understanding
Outputs: a plan to help prevent potential obstacles and increase the chance of continued success
Top tips:
- Imagine the outcome of the proposed project is a disaster
- Generate possible and plausible reasons for the failure
- Revisit the project plan to mitigate identified risks
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Conduct Post-mortem
The review of a project from start to finish to determine what went right and what can be improved, avoiding future challenges
Purpose: to identify those things that most likely led to the failure or success of the proposed improvement
Inputs: Agree Aim Statement, Prioritise Stakeholder Needs, Agree Core Themes, Define Requirements, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Present Case for Change, Review Project Performance, Review Project Progress
Outputs: a review of project delivery and performance to increase the chance of future success
Top tips:
- Celebrate the things that went well and thank the team
- Identify the things that went wrong and learn from mistakes
- Provide closure to the project with a sense of accomplishment
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Synthesise Evidence
The drawing together and summary of a body of evidence that describes the evaluation and selection of concepts for improvement
Purpose: to provide evidence of evaluation of new concepts against the system requirements
Inputs: Define Requirements, Consider Pre-existing Solutions, Stimulate Ideas, Filter Ideas, Develop Concepts, Make Models, Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Barriers, Review Safety, Review Effectiveness, Review Sustainability
Outputs: a clear summary of evidence relating to the evaluation of the new concepts
Top tips:
- Draw together, summarise and communicate all of the evidence
- Do this in a systematic way to support the review criteria
- Use the evidence to support the choice of solution concept
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Case
Making the case is critical to the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important at the beginning of the improvement process and should be reviewed regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process are described within the Improvement Stages section, and each stage will most likely comprise a number of preliminary activities, followed by specific stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the case strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Draft the Pitch. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the case should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The full set of possible activities within the case strand are : Demonstrate Future Improvement, Predict Stakeholder Benefits, Calculate Resources Required, Estimate Time Required and Present Case For Change. If any of these have been undertaken before the start of the project, they should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
The Stage Plan should be used to identify the outputs and deliverables that are required for each stage, and the possible activities that need to be completed. Each improvement stage has its own Stage Guide, which provides guidance on activities that could be selected.
All the activities for the case strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Draft the Pitch
This preliminary activity encourages people to create a simple description of the problem, the process that will solve it, and the benefits that might be achieved and compile the most compelling case to deliver the proposed solution(s) for improving the system.
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Top tips:
- Describe and quantify the scale of the challenge
- Outline the plan for improving the system
- Quantify the likely benefits for patients and stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Demonstrate Future Improvement
The demonstration of most likely behaviour and corresponding improvement to be delivered by the modified system
Purpose: to demonstrate the feasibility of improvement to be delivered by the proposed solutions
Inputs: Define Requirements, Synthesise Evidence, Predict Stakeholder Benefits, Calculate Resources Required, Estimate Time Required
Outputs: a demonstration of the future improvement of the modified system
Top tips:
- Describe the likely future behaviour of the system
- Estimate the level of future behaviour of the system
- Compare the predicted performance against the desired performance
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Predict Stakeholder Benefits
The prediction of most likely behaviour and corresponding benefits to be delivered by the modified system
Purpose: to predict the stakeholder benefits expected by delivering the proposed improvement
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Demonstrate Future Improvement, Calculate Resources Required, Estimate Time Required
Cards: Service Stakeholders
Outputs: a prediction of the stakeholder benefits of the modified system
Top tips:
- Estimate the value of meeting the individual stakeholder needs
- Estimate the value of meeting the system requirements
- Predict the benefit of delivering improvement
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Calculate Resources Required
The calculation of the resources most likely to be required to develop and deliver the modified system
Purpose: to calculate the resources required to develop and deliver the proposed improvement
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Demonstrate Future Improvement, Predict Stakeholder Benefits, Estimate Time Required
Outputs: a calculation of the resources required to deliver the modified system
Top tips:
- Estimate the effort required to meet the system requirements
- Estimate the cost required to meet the system requirements
- Calculate the resources required to deliver improvement
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Estimate Time Required
The estimation of the time most likely to be required to develop and deliver the modified system
Purpose: to estimate the time required to develop and deliver the proposed improvement
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Demonstrate Future Improvement, Predict Stakeholder Benefits, Calculate Resources Required
Outputs: a calculation of the time required to deliver the modified system
Top tips:
- Estimate the effort required to meet the system requirements
- Estimate the time required to meet the system requirements
- Calculate the time required to deliver improvement
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Present Case for Change
The drafting of a case for change, reflecting the system requirements, predicted system performance and likely benefits
Purpose: to present a comprehensive case for change, balancing stakeholder benefits against costs of delivery
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Demonstrate Future Improvement, Predict Stakeholder Benefits, Calculate Resources Required, Estimate Time Required, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: PEST(LE) Analysis, SWOT Analysis, Stakeholder Analysis, The Five Ws and Two Hs, Wardley Map
Outputs: a comprehensive case for change and delivery of the modified system
Top tips:
- Describe the routes to and priorities for enabling improvement
- Identify the support required to deliver demonstrable improvement
- Build a compelling case for the benefits and timeliness of the work
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Plan
Managing the plan is key to the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important at the beginning of the improvement process and should be updated and communicated regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process are described within the Improvement Stages section, and each stage will most likely comprise a number of preliminary activities, followed by specific stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the context strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Decide the Next Step. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the plan should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The full set of possible activities within the plan strand are : Identify Enablers And Blockers, Manage Team, Ensure Shared Understanding, Review Project Performance, Review Project Progress and Plan Future Activities. If any of these have been undertaken before the start of the project, they should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
The Stage Plan should be used to identify the outputs and deliverables that are required for each stage, and the possible activities that need to be completed. Each improvement stage has its own Stage Guide, which provides guidance on activities that could be selected.
All the activities for the plan strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Decide the Next Step
This preliminary activity encourages people to choose the activities most likely to improve the system and enable progress to the next stage gate and deliver the most effective plan to deliver the proposed solution(s) for improving the system.
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Top tips:
- Assess the quality and confidence levels of existing outputs
- Identify the outputs required to pass the next stage gate
- Decide the activities required to reach the next stage gate
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Identify Enablers and Blockers
The identification of stakeholders who have the potential to enhance or disrupt the delivery of an improved system
Purpose: to identify stakeholders who are able to facilitate or block delivery of an improved system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Present Case for Change, Manage Team, Review Project Performance, Review Project Progress, Plan Future Activities, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: SWOT Analysis, Stakeholder Analysis, Gantt Chart, Activity Dependency Diagram
Cards: Service Stakeholders, Service Improvers
Outputs: a list of the enablers and blockers likely to influence the delivery of an improved system
Top tips:
- Identify stakeholders who are most likely to influence a change
- Build on the enthusiasm of actively supportive stakeholders
- Develop strategies to disarm potentially disruptive stakeholders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Manage Team
The assembly and empowerment of a team who have the potential to develop and deliver the modified system
Purpose: to manage a team who are enabled and willing to embark on the programme of improvement
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Present Case for Change, Identify Enablers and Blockers, Ensure Shared Understanding, Review Project Performance, Review Project Progress, Plan Future Activities, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: SWOT Analysis, Stakeholder Analysis, Theory of Change, Gantt Chart, Activity Dependency Diagram, Project Canvas
Cards: Service Improvers
Outputs: a description of the team most likely to deliver the modified system
Top tips:
- Build a team from stakeholders, influencers and facilitators
- Ensure team members are clear of their roles within the programme
- Agree a framework for team communication and meetings
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Review Project Performance
The systematic review of the risks evident in the delivery of an improved system and their likely impact on stakeholders
Purpose: to review risks present in the programme required to deliver an improved system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Present Case for Change, Identify Enablers and Blockers, Manage Team, Ensure Shared Understanding, Review Project Progress, Plan Future Activities, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, Hazard and Operability Analysis, Fault Tree Analysis, Structured What-if Technique, Risk Matrix, SWOT Analysis, Stakeholder Analysis, Theory of Change, Gantt Chart, Activity Dependency Diagram, Project Canvas
Outputs: a list of the hazards present in the programme and the risk they pose to its delivery
Top tips:
- Understand the risks present in the improvement programme
- Estimate the likelihood of disruption posed by these risks
- Identify the likely extent of disruption posed by these risks
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Review Project Progress
The systematic review of progress made in the delivery of an improved system and the likely impact on stakeholders
Purpose: to review progress against the programme required to deliver an improved system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Present Case for Change, Identify Enablers and Blockers, Manage Team, Ensure Shared Understanding, Review Project Performance, Plan Future Activities, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: PEST(LE) Analysis, The Five Ws and Two Hs, Theory of Change, Wardley Map, Driver Diagram, Gantt Chart, Activity Dependency Diagram, Project Canvas
Worksheets: Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan, Activity Plan
Outputs: a review of the progress made against the planned programme delivery targets
Top tips:
- Understand the progress made in the improvement programme
- Review the progress made against the plan of future activities
- Identify areas where progress is not in line with that planned
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Plan Future Activities
The development of a resilient plan for the timely and cost effective delivery of an improved system
Purpose: to plan the next steps in a clear and robust programme to deliver an improved system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Present Case for Change, Identify Enablers and Blockers, Manage Team, Ensure Shared Understanding, Review Project Performance, Review Project Progress, Agree Aim Statement
Tools: PEST(LE) Analysis, The Five Ws and Two Hs, Theory of Change, Wardley Map, Driver Diagram, Gantt Chart, Activity Dependency Diagram, Project Canvas
Worksheets: Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan, Activity Plan
Posters: Stage Activities
Outputs: a detailed plan of the next steps required to deliver an improved system
Top tips:
- Establish a clear and effective planning and reporting process
- Define clear targets for each stage of the improvement process
- Deliver regular progress updates to the programme funders
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Scope
Agreeing the scope is vital to the successful delivery of an improvement project. This is particularly important at the beginning of the improvement process and should be challenged regularly throughout the process.
The Initiate, Understand, Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages of an improvement process are described within the Improvement Stages section, and each stage will most likely comprise a number of preliminary activities, followed by specific stage activities.
The preliminary activity for the scope strand of the Initiate and Understand stages is Challenge the Scope. This provides useful input to the Improvement Canvas and should be completed (to at least some degree). For the Co-design, Deliver and Sustain stages, the scope should be reviewed and updated as necessary to support the ongoing improvement process.
The remaining activity within the scope strand is: Agree Aim Statement. If this has been undertaken before the start of the project, it should be reviewed within the Initiate Stage or Understand Stage.
All the activities for the scope strand are now described in detail, together with the tools that may be used to support them.
Challenge the Scope
This preliminary activity encourages people to consider different levels of scope and pick the most appropriate level for the project to succeed and discuss the most appropriate programme scope to respond to the proposed solution(s) for improving the system.
Worksheets: Stakeholder Map, Improvement Canvas, Stage Plan
Posters: Questions Map
Top tips:
- Expand the scope by asking why does this happen?
- Consider the balance of risk and reward for different levels of scope
- Review the system sketches and identify what is in or out of scope
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Agree Aim Statement
The drafting and communication of an agreed statement of purpose and direction of improvement for the system
Purpose: to agree and communicate a clear description of the overall aim for improvement of the system
Inputs: Define Requirements, Develop Concepts, Synthesise Evidence, Present Case for Change
Worksheets: Improvement Canvas
Outputs: a succinct statement describing the overall aim for improvement of the system
Top tips:
- Consult likely stakeholders and influencers to define the aim
- Define realistic targets for the overall improvement process
- Establish a clear and effective communication strategy
Back to text list of Activities | Back to pictorial list of Activities
Feedback
We would welcome your feedback on this page:
Privacy policy. If your feedback comments warrant follow-up communication, we will send you an email using the details you have provided. Feedback comments are anonymized and then stored on our file server
Read more about how we use your personal data. Any e-mails that are sent or received are stored on our mail server for up to 24 months.