The evidence describes the information in support of solution(s) within a system and the means used to measure the performance of the system.
Contents
Introduction
The need to Collect the Evidence is the fourth of the seven strands in the improvement model. It underlines the importance of collecting the evidence that the system has been improved, following understanding the system, defining the problem and developing the solution. As a result, it is expected that such a definition will be developed in the intermediate stages of the improvement process and revised, as appropriate, as the process develops.
Purpose
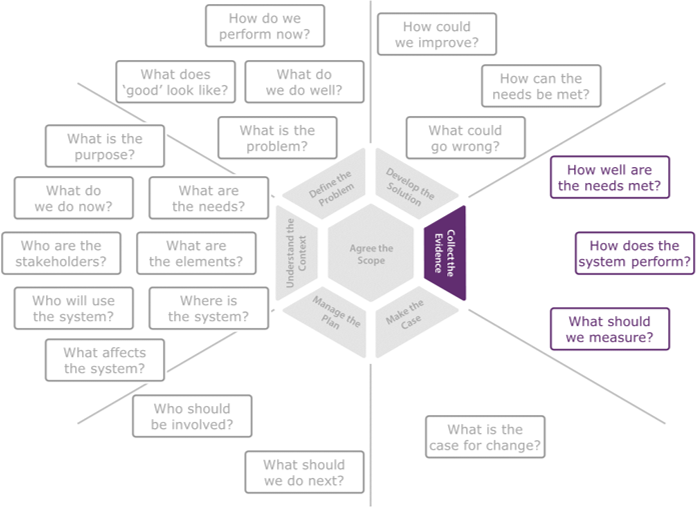
Collecting the evidence has particular importance to systems improvement: defining the measures required to evaluate the performance of the system of interest; undertaking a range of evaluation activities to evaluate effectiveness, patient safety and patient experience; and synthesising the information to evidence the extent of the improvement to the system.
Activities
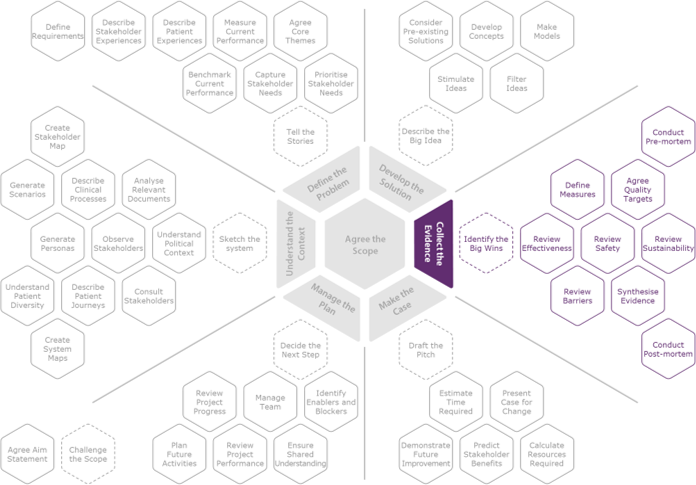
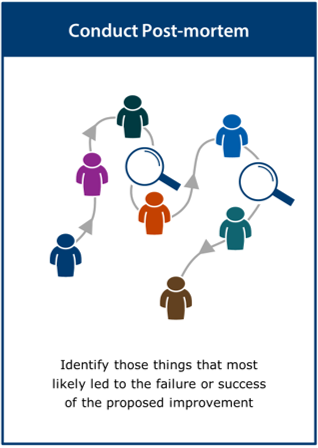
The process of collecting the evidence may include a wide range of activities including, but not limited to: Define Measures, Agree Quality Targets, Review Effectiveness, Review Safety, Review Barriers, Review Sustainability, Conduct Pre-mortem, Conduct Post-mortem and Synthesise Evidence.
In the Initiate and Understand stages of the improvement process, a preliminary activity, Identify the Big Wins, provides a useful starting point. It may also be relevant for the Co-design, Delivery and Sustain stages, where the context should be reviewed and updated to support the changing priorities of the latter stages of the improvement process.
More detail on each of these activities is given in the collect the evidence part of the Activities section (within Resources)
Tools
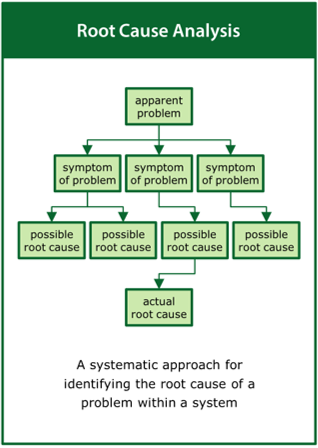
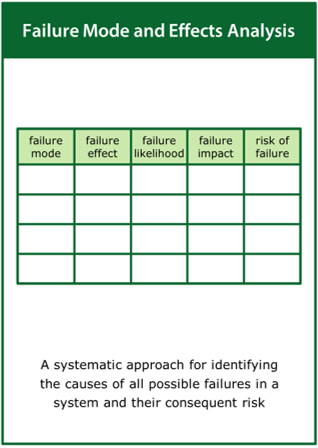
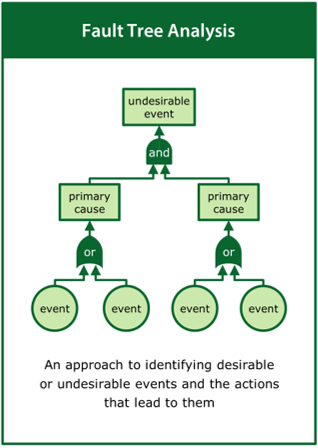
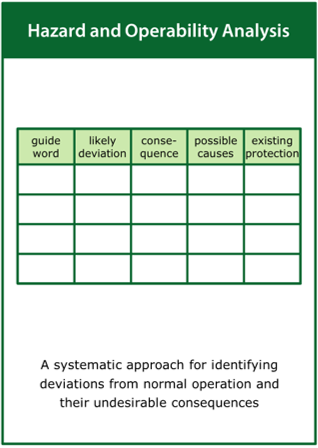
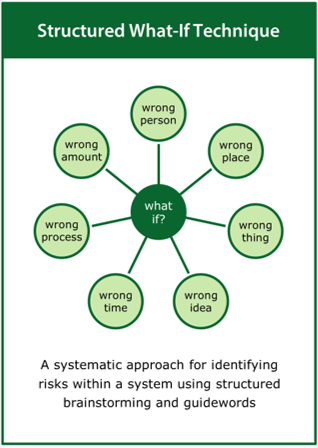
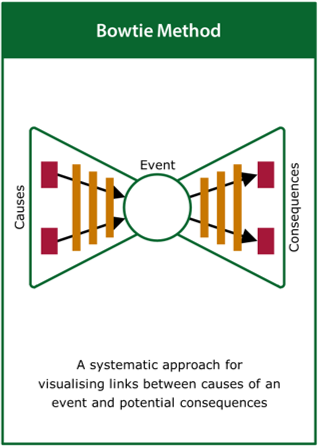
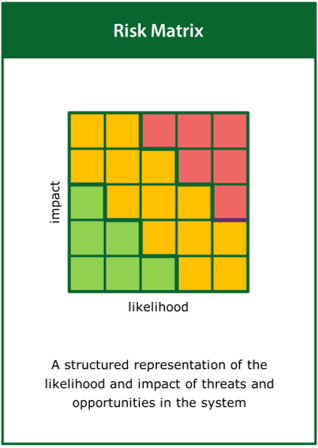
The practice of collecting the evidence may draw on a wide range of tools including, but not limited to: Exclusion Audit, User Trials, Expert Review, Life Cycle Assessment, Root Cause Analysis, Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, Fault Tree Analysis, Structured What-if Technique and Risk Matrix.
More detail on each of these activities is given in the collect the evidence part of the Tools section (within Resources)
Use the Questions Map poster to identify the key questions that would help to deliver the outputs required.
Alternatively, use the Stage Activities poster to identify the improvement activities that would help deliver the outputs required.
Activities
Tools
Feedback
We would welcome your feedback on this page:
Privacy policy. If your feedback comments warrant follow-up communication, we will send you an email using the details you have provided. Feedback comments are anonymized and then stored on our file server
Read more about how we use your personal data. Any e-mails that are sent or received are stored on our mail server for up to 24 months.